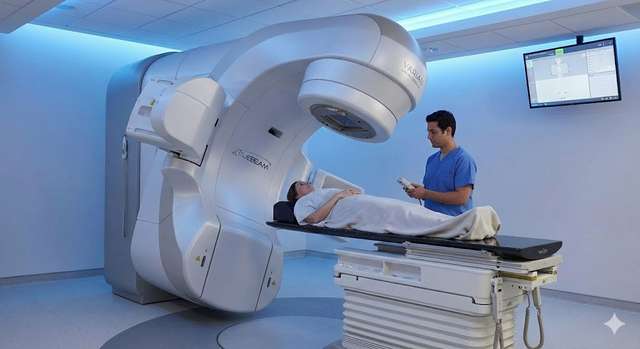
VARIAN TRUEBEAM RADIOTHERAPY PACKAGE
Advanced external beam radiotherapy using the Varian TrueBeam system with HyperArc for ultra-precise intracranial radiosurgery.
The TrueBeam linear accelerator is among the world’s most advanced platforms for IGRT, IMRT, and radiosurgery. It delivers high accuracy (<0.95 mm), fast imaging guidance, and HyperArc technology for treating multiple brain metastases within minutes. Suitable for a wide variety of tumors.
Treatment: External Beam Radiotherapy (TrueBeam)
Indications:
-
Nasopharyngeal cancer
-
Head & neck tumors
-
CNS tumors
-
Lung & esophageal cancers
-
Prostate, rectal, endometrial cancers
-
Primary liver cancers
Features:
-
Non-invasive, painless, short recovery
-
Only 1–5 sessions for SRS
-
Sub-millimeter accuracy
-
Minimal normal tissue damage
-
Suitable for benign & malignant tumors
About The Package
Advanced external beam radiotherapy using the Varian TrueBeam system with HyperArc for ultra-precise intracranial radiosurgery.
The TrueBeam linear accelerator is among the world’s most advanced platforms for IGRT, IMRT, and radiosurgery. It delivers high accuracy (<0.95 mm), fast imaging guidance, and HyperArc technology for treating multiple brain metastases within minutes. Suitable for a wide variety of tumors.
Treatment: External Beam Radiotherapy (TrueBeam)
Indications:
-
Nasopharyngeal cancer
-
Head & neck tumors
-
CNS tumors
-
Lung & esophageal cancers
-
Prostate, rectal, endometrial cancers
-
Primary liver cancers
Features:
-
Non-invasive, painless, short recovery
-
Only 1–5 sessions for SRS
-
Sub-millimeter accuracy
-
Minimal normal tissue damage
-
Suitable for benign & malignant tumors
Hospital
Inclusions & Exclusions
Inclusions
Radiotherapy planning
Daily imaging
Interpreter
Follow-up review
Exclusions
PET/CT if required
-
Medication
-
Additional specialist consults
About The Treatment
Radiation therapy, also known as radiotherapy, is not a disease but a treatment method used in the management of various medical conditions, primarily cancer. It works by using high-energy particles or waves, such as X-rays, gamma rays, electron beams, or protons, to destroy or damage cancer cells. Radiation therapy is effective because it can target specific areas of the body where cancer cells are located, minimizing damage to the surrounding healthy tissues.
Key Aspects of Radiation Therapy:
Purpose: Primarily used to treat cancer, including breast, lung, prostate, and brain cancers, as well as to reduce symptoms and improve quality of life in cases of advanced cancer.
Types: There are two main types of radiation therapy:
- External beam radiation therapy (EBRT): Involves a machine outside the body that directs radiation beams at cancerous areas.
- Internal radiation therapy (brachytherapy): Involves placing a radioactive material inside the body near cancer cells.
Procedure: Treatment is typically spread over several sessions, and the total number and frequency depend on the type and stage of cancer. External therapy is usually outpatient, taking only a few minutes per session, whereas internal therapy may require a brief hospital stay.
Side Effects: Common side effects include fatigue, skin irritation at the treatment site, and more specific effects depending on the area being treated, such as hair loss when the head is targeted or digestive issues when the abdomen is involved. Long-term effects might include the risk of developing a second cancer or damage to nearby organs and tissues.
Effectiveness: The effectiveness of radiation therapy varies based on the type and stage of cancer, overall health of the patient, and the goal of treatment, whether it is curative, palliative, or adjuvant (in combination with other treatments like surgery and chemotherapy).
Purpose: Primarily used to treat cancer, including breast, lung, prostate, and brain cancers, as well as to reduce symptoms and improve quality of life in cases of advanced cancer.
Types: There are two main types of radiation therapy:
- External beam radiation therapy (EBRT): Involves a machine outside the body that directs radiation beams at cancerous areas.
- Internal radiation therapy (brachytherapy): Involves placing a radioactive material inside the body near cancer cells.
Procedure: Treatment is typically spread over several sessions, and the total number and frequency depend on the type and stage of cancer. External therapy is usually outpatient, taking only a few minutes per session, whereas internal therapy may require a brief hospital stay.
Side Effects: Common side effects include fatigue, skin irritation at the treatment site, and more specific effects depending on the area being treated, such as hair loss when the head is targeted or digestive issues when the abdomen is involved. Long-term effects might include the risk of developing a second cancer or damage to nearby organs and tissues.
Effectiveness: The effectiveness of radiation therapy varies based on the type and stage of cancer, overall health of the patient, and the goal of treatment, whether it is curative, palliative, or adjuvant (in combination with other treatments like surgery and chemotherapy).
